Calculate the electric field along the axis at a distance x from the center of a charged disk with radius R.
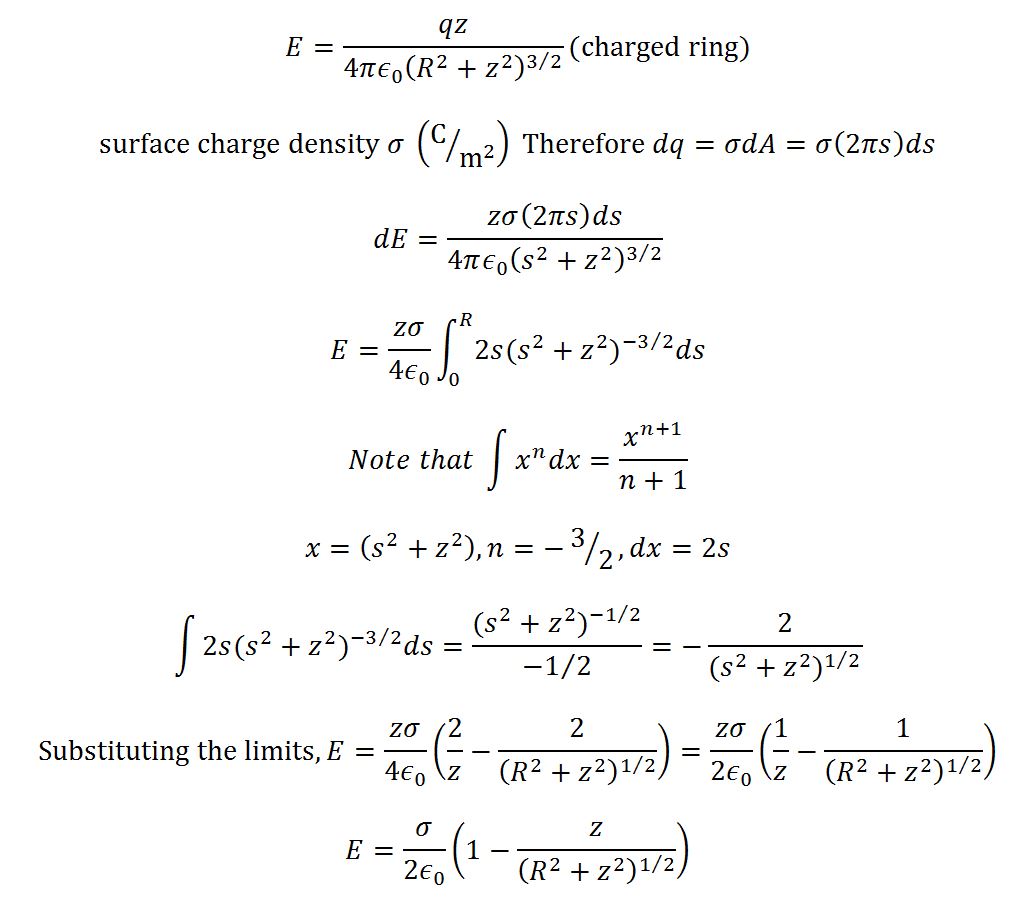
Charge is quantized. The elementary charge has the value:
e = 1.60×10-19C
SP2. A penny, being electrically neutral, contains equal amounts of positive and negative charge. What is the magnitude of these equal charges?
Mpenny = 3.1g
Atomic mass of copper = 63.546 amu
Atomic number of copper = 29
1 amu = 1.66×10-24g
Answer is ~136,000C